
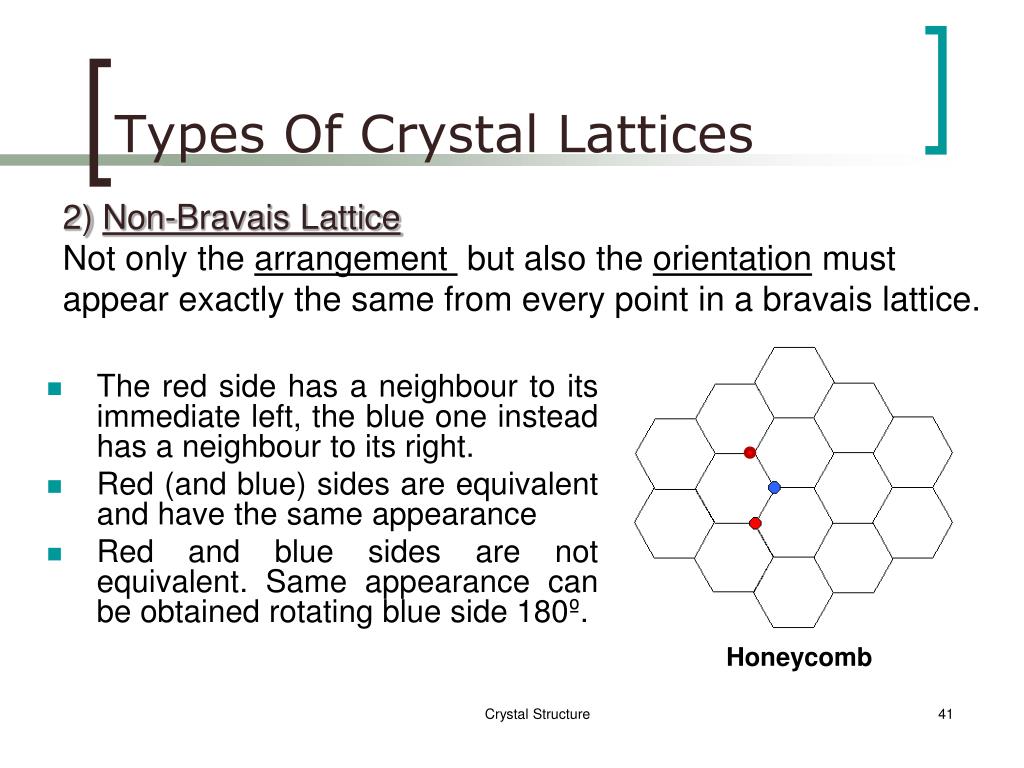
This primitive cell does not always show the clear symmetry of a given crystal. R = n 1 a 1 + n 2 a 2 + n 3 a 3, is the chosen primitive vector. In geometry and crystallography, a Bravais lattice, named after Auguste Bravais ( 1850), is an infinite array of discrete points generated by a set of discrete translation operations described in three dimensional space by They can also used to create designs in textiles, architecture, and other art forms.The seven lattice systems and their Bravais lattices in three dimensions Lattices can used to model a variety of repeating patterns in nature, such as crystals and honeycombs.The points can connected by straight lines, forming a lattice pattern. A lattice is a two-dimensional grid of points, arranged in a regular, repeating pattern.However a lattice is a group of points in a plane or space that connected by line segments. Lattice theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of lattices and also their applications.

Other types of symmetry include tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombohedral, and also orthorhombic. The most common type of symmetry is cubic symmetry, which used to describe most crystals. Therefore 14 different types of symmetry that can used to describe a lattice, and each type of symmetry has a different name. The word “lattice” comes from the Latin word for “lattice,” which means “a network of crossed or intertwined beams or bars.” However the structure of a lattice often described by its symmetry, which is a measure of how the lattice points arranged in space. Therefore the development of X-ray crystallography in the early 20th century was a major advance in crystallography and has used to determine the structures of thousands of crystals.Ī lattice is a repeating, three-dimensional structure made up of smaller units called lattice points.
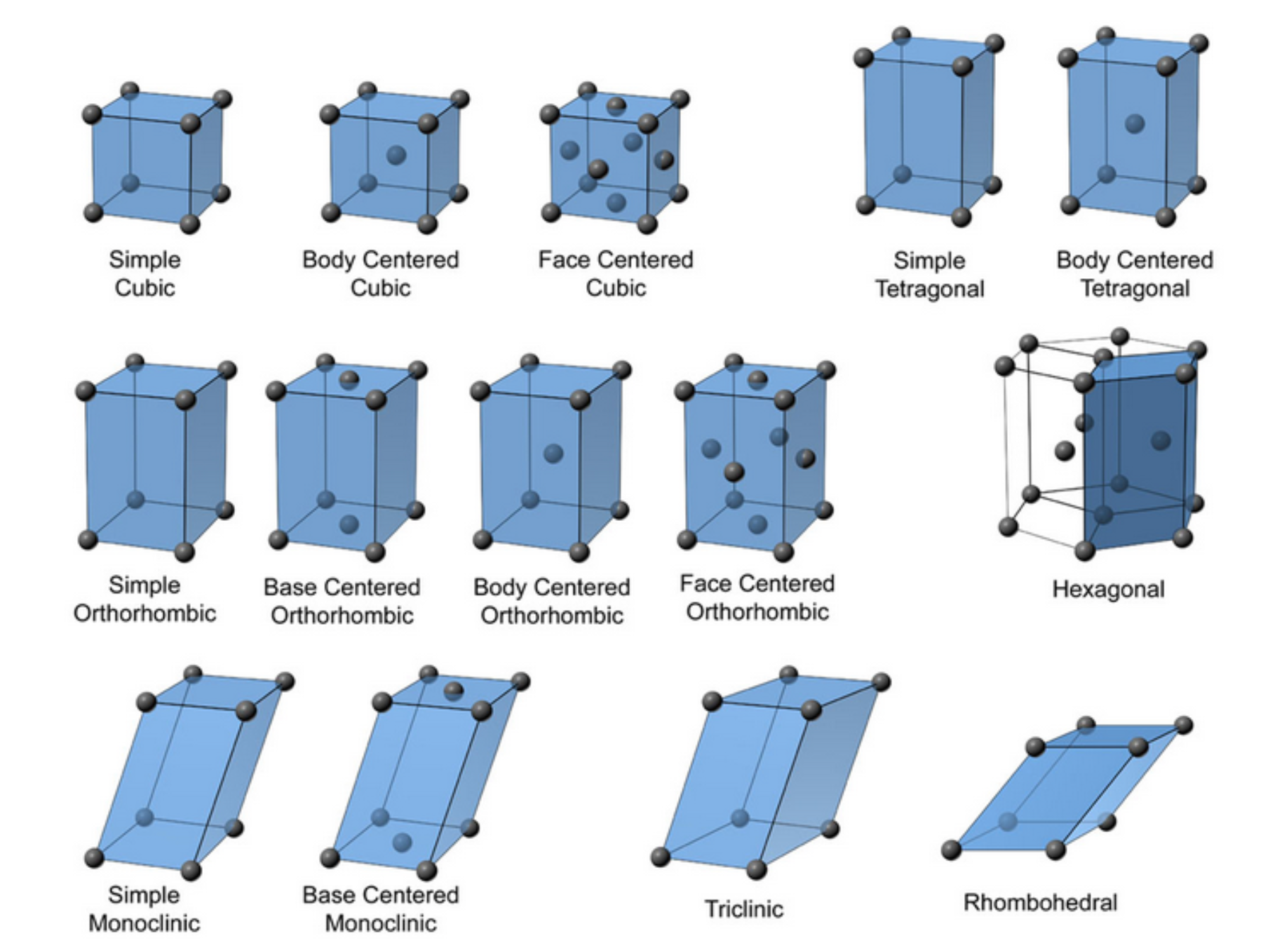

Rhombic: The molecules arranged in a rhombic pattern.Octahedral: The molecules arranged in an octahedral pattern.Hexagonal: The molecules arranged in a hexagonal pattern.Tetrahedral: The molecules arranged in a tetrahedron-like pattern.There are seven crystal systems, which determined by the way the crystal molecules arranged.Ĭubic: The molecules arranged in a cube-like pattern. Quasi-crystal lattice: A quasi-crystal lattice formed when the atoms in a crystal lattice joined together by ionic bonds. Molecular lattice: A molecular lattice formed when the atoms in a crystal lattice joined together by covalent bonds.ģ. The atoms in a crystal lattice are held together by chemical bonds.Ģ. Crystal lattice: In a crystal lattice, the atoms are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern. There are three types of lattice structures:ġ.
The unit cell is the basic building block of a crystal and its shape is determined by the chemical composition and also arrangement of its atoms. Some common examples of crystals include diamond, quartz, and also salt.Ī unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
